How to identify blocking processes/long running queries in SQL server?
Blocking occurs when a process hold a lock and other process has to wait till the first process completes.
Sometime, when we execute any stored procedures or a query and expect that to complete quickly but it kept running for a long time in this situation we do not have any other option rather than stopping a query or stored procedure, It just happens due to process block issues.
Lets try to understand it with the help of an example.
To implement a blocked processes scenario, we will try to update one record in a table under begin tran block but will not commit the transaction that will hold update lock on a table and process kept running until transaction is not committed and during that time we will update same record in another session .
As you can see, we have updated a record in a table under begin transaction block but not committed yet.
use Sqltutorials Begin Tran update dbo.Customer set firstName = 'Jon M' where customerKey =11000
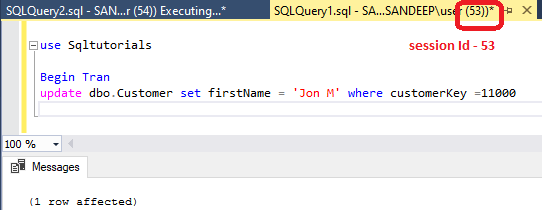
Now, open another query editor window ) and try to update same record in a table and you see the update query keep running and not updating record.
use Sqltutorials update dbo.Customer set firstName = 'Jon M' where customerKey =11000

Lets identify the those blocking processes .
You can execute SP_who2 to get the blocked processes details.
As, you can see blkby is – 53, it means processes Id -53 (That is first query where you have ran a update query under begin transaction but not committed ) is blocking the execution of processes Id – 54 ( that is second query ) .
sp_who2
Exec sp_who2

Here, we identified that the processes id is blocking the second query execution so we can kill the processes id -53, using kill spid command as given below
kill 53

As soon as we kill the blocked processes, the second query executed successfully and update the record.

We can also use SysProcesses to get the blocked processes details –
SELECT spid,
blocked as blockingProcessesId,
(SELECT Systxt1.TEXT
FROM sysprocesses st
CROSS apply sys.Dm_exec_sql_text(sql_handle) systxt1
WHERE spid = p.blocked) AS blockingQuerytxt,
PROGRAM_NAME, loginame, DB_NAME(p.dbid) as DatabaseName,
Systxt2.TEXT as Querytxt
FROM sysprocesses p
CROSS apply sys.Dm_exec_sql_text(sql_handle) Systxt2
WHERE blocked <> 0

![]()
